Sept. 22, 2025
A recently published research paper evaluating the integration of infectious disease screening, prevention, and treatment in a hospital based inpatient substance use treatment program included contributions from C Change Senior Project Manager, Hannah Zellman, who is a co-author on the paper.
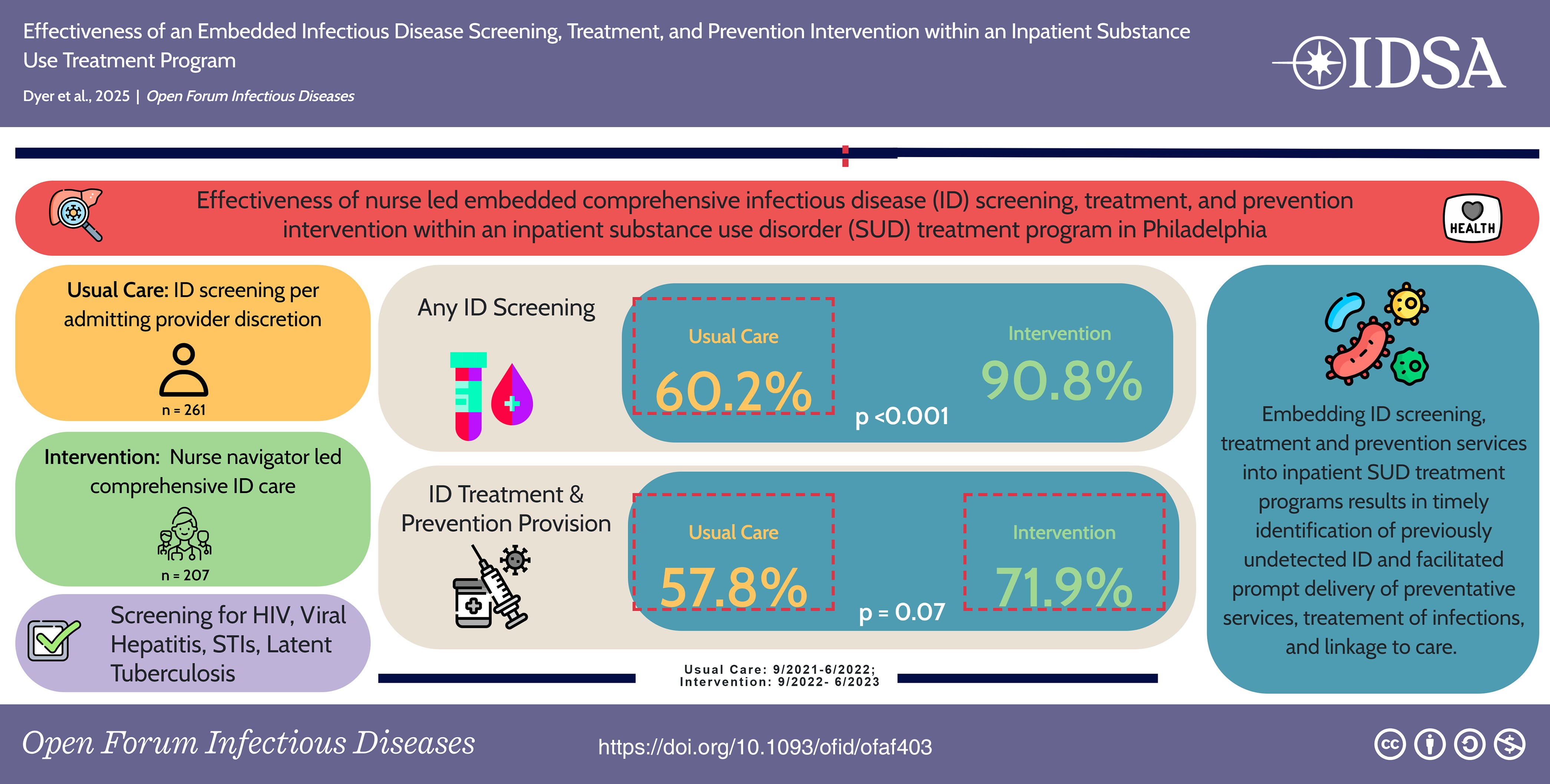
The paper, published in the August 2025 issue of the journal Open Forum Infectious Diseases, is titled Effectiveness of an Embedded Infectious Disease Screening, Treatment, and Prevention Intervention Within an Inpatient Substance Use Treatment Program. Its primary author is Dr. Kelly E. Dyer of the University of Pennsylvania Health System Division of Infectious Diseases, with 11 co-authors credited.
An effectiveness study was conducted evaluating a comprehensive infectious disease screening, prevention, and treatment intervention at an inpatient substance use treatment unit at Penn Presbyterian Medical Center, an affiliate hospital of the University of Pennsylvania Health System.
The role of the Health Federation of Philadelphia’s C Change program in this effort, Zellman said, was to provide education and training for medical providers and frontline staff on HIV and viral hepatitis. C Change also led technical assistance activities to develop and optimize workflows, establish referral pathways, and ensure that all staff were equipped with tools and best practices for connecting patients to prevention and treatment.
“Building HIV and viral hepatitis screening programs may seem straightforward, but it takes time and infrastructure to do so,” Zellman said. “Getting someone from screening to care is a heavy lift, especially when a patient's time in the program is limited.”
Zellman said that “C Change works in partnership with the viral hepatitis program at PDPH (the Philadelphia Department of Public Health) to bring technical assistance directly to settings we are working with.” A hallmark of C Change’s work is blending clinician training, education, and workflow development. “We take it from knowledge to practice,” she said.
C Change’s medical director, Dr. Stacey Trooskin, led clinical training efforts and provided ongoing case consultation for medical providers. Dr. Trooskin worked alongside Zellman and C Change Program Coordinator Kayla Gray to build systems for patient monitoring and workflow optimization.
During the study, patients met with a nurse navigator trained in infectious disease care, and had screenings for HIV and viral hepatitis, as well as sexually transmitted infections and tuberculosis based on exposure history. A “usual care” period at the inpatient unit without comprehensive infectious disease testing was also analyzed before the study period for comparison purposes.
Infectious disease screening test completions increased from 60.2% during the usual care period to 90.8% during the study period, with infectious disease treatment and prevention provision increasing from 57.8% to 71.9% during the study period.
Speaking about the positive results from the study, Zellman said “It's exciting to have strong evidence proving what we know: embedding infectious disease services into settings serving people who use drugs works.”
The work of C Change going forward will continue to focus on supporting settings serving people who use drugs in efforts to integrate HIV and viral hepatitis prevention, screening, and treatment services , with plans to continue similar work with substance use disorder treatment settings in the Philadelphia region. Since 2017, C Change has been a close partner of the Philadelphia Department of Public Health working on related initiatives.
“There have been significant changes to hepatitis C in recent years. Treatment restrictions have been rolled back, and treatment guidelines have been simplified,” Zellman said. With recent developments in hepatitis C diagnostic technology, hepatitis C can be diagnosed in around 60 minutes using whole blood from a finger stick. Zellman explained, “we’re trying to get as close to a test-and-treat model as possible.”
Study co-authors included professionals from the Philadelphia Department of Public Health’s viral hepatitis program; the University of Pennsylvania Health System’s Division of General Internal Medicine and Division of Psychiatry; and University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine’s the Department of Biostatistics, Epidemiology, and Informatics, Center for Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, and Center for Real-world Effectiveness and Safety of Therapeutics.
--
About the Health Federation of Philadelphia
The Health Federation of Philadelphia is a public health nonprofit that promotes community health by advancing access to high-quality, integrated, comprehensive health and human services.
The Health Federation of Philadelphia serves as a keystone supporting a network of Community Health Centers as well as the broader base of public and private-sector organizations that deliver healthcare, public health and human services to vulnerable populations.

